> The importance of building orientation
Last updated 10:24 pm, Sunday 17th January 2021
The solar orientation of a building is important to its overall energy efficiency. This article explains this in detail and describes the steps you need to take to get best benefit from the correct solar orientation. This could save you thousands whilst reducing your impact on the environment.
A correctly orientated building can save a lot of money in no longer required heating and cooling costs expenditure - in effect the building itself maintains a comfortable environment for you with little additional costs. This is especially relevant with rising fuels bills and the increasing costs of electricity. By simply building this way, a house can reduce its heating and cooling costs by 85%!
An extra benefit is that there is nothing as such to break down or fail with the orientation, hence it being called 'Passive Solar', so nearly zero maintenance costs to incur during the lifetime of the building.
BTW Passive Solar design is nothing new, people having been doing it for thousands of years in numerous cultures, we have just given it a fancy name of late. In fact one of earliest references to Passive Solar principals was by Socrates some 2,300 years ago...
“Now in houses with a south aspect, the sun’s rays penetrate into the porticos in winter, but in the summer the path of the sun is right over our heads and above the roof, so that there is shade. If, then, this is the best arrangement, we should build the south side loftier to get the winter sun and the north side lower to keep out the winter winds.”
So the ancient Greek's knew the power of Passive Solar and how to harness it, and once you finish reading this article on building orientation, so will you!
Orientate your building to use the Sun to your advantage
The fact the Sun is lower in the sky in Winter than in Summer allows us to plan and construct buildings that capture that free heat in Winter and reject the unneeded heat in Summer. The solar orientation of the whole building plays an important part in ensuring such a 'passive' process works consistently. Please refer to the diagram below for an explanation.
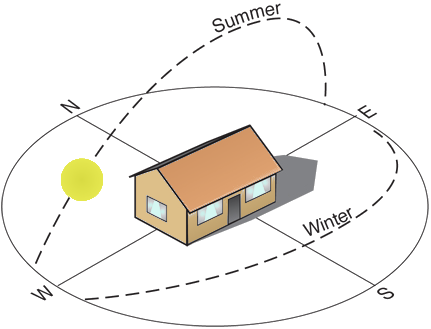
The 'trick' with Passive Solar is in Summer to use shade to block the Sun heating up the interior of the property, but do so that is just enough to to stop it; then when the Sun goes lower in the Winter that shade is no longer enough to prevent the Sun coming into the property and you get free heat just when you need it.
Ideal house orientation
The ideal house solar orientation for Passive Solar benefit is that the main long axis of the building runs East-West, i.e the ridge line. You can move this by as much as 20 degrees without ill effect, but the most glass on the building must be facing towards the Sun.When deciding the building orientation also take into account the location of landscape features on your plot , i.e. trees and walls, etc which will impact on how you harness the Sun. Ideally you do not want them blocking the Sun light as the Sun tracks across the sky in Winter. So trees with high branches as especially beneficial if placed to the East or West of the building, as they will shade in Summer let allow the Sun light through in Winter.
Solar orientation is different to magnetic orientation
It is very important that you remember to orientate your house with respect to the Sun and not to the magnetic North (or South), see the diagram below.
Apparent magnetic North can be very different to where Solar North actually is (up to 20 degrees), this difference between magnetic orientation and solar orientation can make all the difference between a passive solar design being viable or not. Your local council should be able to give you details of what the offset should be as this varies from place to place.
Living Area placement
Also of importance is that the rooms most used must be on the side of the house orientated towards the Sun, i.e. the kitchen, lounge, etc. Also put the least used rooms on the side of the house in shade, i.e. garage, laundry; these will also act as additional thermal mass, if properly insulated. Also by putting your most used rooms on one side of the building means you can effectively 'close off' the part of the house you do not use, again avoiding heating/cooling & lighting costs. It also means that the rooms you use most receive the most natural light, thereby also reducing your lighting costs.
As a result Passive Solar homes often have a 'lived in' side and a side of the house that be closed off (using doors typically) when not in use. Also Passive Solar homes are rarely open plan throughout as this defeats the whole intention of Passive Solar.
Design your house for the whole year
Since you live in your home through Summer and Winter, you should design it for the entire year. It is important to be comfortable all year long and not just for a single season. Sometimes, solar homes are built with large areas of upward, tilted, south-facing glass, designed to catch every bit of Sun, Winter or Summer. While tilted glass does maximize heat gain during the winter months, it also maximizes that same heat gain during the Summer. If you understand that the rays of Sun's high Summer arc will bounce off vertical, south-facing glass and reduce heat gain, you can let nature do the work for you in a passively designed home, read this article on how to do it.
More advice and key information on the next page.
- Pages:
- 1
- 2
- Next page »
Related Tags: building orientation, solar orientation, passive solar, sustainable architecture, sustainable design, home, home design, passive design, solar house
Related Listings: Insulation, Green Architects
